LinkedIn MATLAB Assessment Answers 2021
Are you searching for LinkedIn MATLAB Assessment Answers? You're lending at the right place, here you will get 100% correct answers from the experts.
Bookmark this blog for all your future answer references. Choose the correct linkedin quiz answer highlighted with "Blue" text.
MATLAB: A Practical Introduction to Programming and Problem Solving
LinkedIn MATLAB Assessment Questions and Answers 2021
Q1. From what distribution does the rand() function return value?
- normal
- poisson
- binomial
- uniform
Q2. Based on the code below, c is the \_ of a.
a = rand(1, 11);
b = sort(a);
c = b(1, ceil(end/2));
- median
- mode
- mean
- margin
Q3. What does the Profiler track?
- execution time
- command history
- errors
- the value of variables
Q4. Which code block contains the correct syntax for a while loop?
- [ ] a = 0;
do
a = a + 1;
while a < 5
end
- [ ]
a = 0;
while(a < 5)
a = a + 1;
- [ ]
a = 0;
while a < 5:
a = a + 1;
- [x]
a = 0;
while a < 5
a = a + 1;
end
Q5. What does b contain?
a =
19 20 12 0 6
6 9 56 0 3
46 8 9 8 19
9 8 8 19 46
1 9 46 6 19
[x] b =
56 0
9 8
[ ] b =
8 19
19 46
Q6. You have written a function myfun and want to measure how long it takes to run. Which code segment will return in t the time in seconds it takes myfun to run?
- [ ] t = cputime(myfun());
- [x] tic;
myfun();
toc;
- [ ] timer.start;
myfun()
t = timer.stop;
- [ ] t = timer(myfun());
Q7. What is %% used for?
- argument placeholder
- block quotes
- code sections
- conversion specifier
Q8. what is the . character NOT used for?
- structure field access
- a decimal point
- cell array access
- element-wise operations
Q9. Which function could you use for multiple linear regression?
- polyval
- regress
- solve
- polyfit
Q10. For which of these arrays do mean, median, and mode return the same value?
- [0 1 1 1 2]
- [1 3 5 5 6]
- [0 1 1 1 1]
- [0 0 5 5 5]
Q11. You are in the middle of a long MATLAB session where you have performed many analyses and made many plots. You run the following commands, yet a figure window doesn't pop up on the top of your screen with your plot. What might be the issue?
x = [-1:0.1:1];
y = X.^2;
plot(x, y)
- Your plot doesn't plot in a figure window because figure was not called immediately in advance.
- Your plot syntax is incorrect.
- Your plot is in a figure window that was already open, hidden behind other windows on your screen.
- Your plot was saved to an image file but not displayed.
Read More About: How To Take Linkedin Skill Assessment Quiz in 2022
Q12. How do you access the value for the field name in structure S?
- S['name']
- S.name
- S('name')
- S{'name'}
Q13. What built-in definition does i have?
- basic imaginary unit
- index function
- infinity
- index variable
Q14. Which statement is equivalent to this for loop?
a = [1 2 3; 4 5 6];
b = zeros(size(a));
for i_row = 1:size(a, 1)
for i_col = 1:size(a, 2)
b(i_row, i_col) = a(i_row, i_col)^2;
end
end
- b = a*a;
- b = a.^2;
- b = a^2;
- b = pow2(a);
Q15. You have plotted values of cosine from -10 to 10 and want to change the x-axis tick marks to every pi, from -3pi to 3pi. Which statement will do that?
- xticks(-3pi:3.14:3pi)
- xticks(-3pi:pi:3pi)
- xticks(linespace(-3pi(), 3pi(), pi()))
- xticks(linespace(-3pi, 3pi, pi)
Q16. What is the value of c?
a = ones(1,3);
b = 1:3;
c = conv(a,b)
- [-1 2 -1]
- [1 3 6 5 3]
- 6
- [1 -2 1]
Q17. Which function CANNOT be used to randomly sample data?
- datasample
- randi
- resample
- randperm
Q18. Which choice is correct syntax for a switch statement?
- [x] x = 7;
switch x
case 2
disp("two");
otherwise
disp("not two");
end
- [ ] x = 7;
switch x :
case 2
disp("two");
otherwise
disp("not two");
end
- [ ] x = 7;
switch x
case 2
disp("two");
else
disp("not two");
end
- [ ] x = 7;
switch x
case 2
disp("two");
default
disp("not two");
end
Q19. What is the result of this code?
a = 1;
b = 2;
c = 3;
d = 4;
e = c / (~a - b == c - d);
Error
- [ ] c =
NaN
- [x] c =
Inf
- [ ] c =
-0.2500
Q20. What is true of a handle class object?
- When you pass a handle object to a function, a new object is made that is independent of the original.
- All copies of handle objects refer to the same underlying object.
- Handle object cannot reference one another.
- Handle object do not have a default eq function.
Q21. Which choice has a different final result in f10 than the other three?
- [ ] f10 = 1;
for i = 1:10
f10 = f10 * i;
end
- [ ] f10 = factorial(10)
- [x] f10 = 1;
i = 1;
while i <= 10
i = i + 1;
f10 = i * f10;
end
- [ ] f10 = prod(1:10)
Q22. Which choice will NOT give you a 5 x 5 identity matrix?
- [ ] a = rand(5);
round(a * inv(a))
- [ ] diag(ones(5, 1))
- [ ] identity(5)
- [ ] eye(5)
Q23. Which statement creates this structure?
dog =
name: 'Bindy'
breed: 'border collie'
weight: 32
dog = struct('name', 'Bindy'; 'breed', 'border collie'; 'weight', 32);
- [x]
dog.name = 'Bindy';
dog.breed = 'border collie';
dog.weight = 32;
- [ ]
dog = {
'name' : 'Bindy',
'breed' : 'border collie',
'weight': 32;
}
- [ ]
dog('name') = 'Bindy';
dog('breed') = 'border collie';
dog('weight') = 32;
Q24. my_func is a function as follows. What is the value of an at the end of the code beneath?
function a = my_func(a)
a = a + 1;
end
------------------
a = 0;
for i = 1:3
my_func(a);
end
a = my_func(a);
- 4
- 3
- 0
- 1
Q25. Which statement could create this cell array?
c =
{["hello world"]} {1×1 cell} {["goodbye"]} {1×3 double}
- c = {"hello world" {"hello"} "goodbye" [1 2 ]};
- c = {"hello world" {"hello"} "goodbye" {[1 2 3]}};
- c = {"hello world" {"hello"} "goodbye" [1 2 3]};
- c = {"hello world" {"hello" "hello"} "goodbye" {[1 2 3]}};
Read More About: Are Linkedin Skill Assessments Worth It in 2022
Q26. Which choice adds b to each row of a?
a = ones(4, 4);
b= [1 2 3 4];
- a = a + reshape(b, 4, 1);
- a = a + b';
- a = a + repmat(b, 4, 1);
- a = a + [b b b b];
Q27. Which choice replaces all as with os?
- [ ] for i = 1:length(fruit)
fruit{i}(fruit{i} == a) == o;
end
- [ ] for i = 1:length(fruit)
fruit(i)(fruit(i) == 'a') == 'o';
end
- [x] for i = 1:length(fruit)
fruit{i}(fruit{i} == 'a') == 'o';
end
- [ ] for i = 1:length(fruit)
fruit{i}(fruit{i} == 'a') == 'o';
Q28. Which statement returns the roots for the polynomial x^2 + 2x - 4?
- poly([1 2 -4])
- solve(x^2 + 2x - 4 == 0)
- polyfit(x^2 + 2x - 4 == 0)
- roots([1 2 -4])
Q29. Which choice is the proper syntax to append a new elements a to the end of 1x 2 dimensional cell array C?
- C = {C a};
- C = cellcat(C a)
- C = cat(2, {a}, C)
- C{end+1}=a
Q30. You have loaded a dataset of people's heights into a 100 x 1 array called height. Which statement will return a 100 x 1 array, sim_height, with values from a normal distribution with the same mean and variance as your height data?
- sim_height = std(height) + mean(height) * randn(100, 1);
- sim_height = mean(height) + std(height) * randn(100, 1);
- sim_height = randn(std(height), mean(height), [100, 1]);
- sim_height = randn(mean(height), std(height), [100, 1]);
Q31. Which statement returns a cell array of the strings containing 'burger' from menu?
menu = {'hot dog' 'corn dog' 'regular burger' 'cheeseburger' 'veggie burger'}
- menu{strfind(menu, 'burger')}
- menu(strfind(menu, 'burger'))
- menu{contains(menu, 'burger')}
- menu(contains(menu, 'burger'))
Q32. What is the set of possible values that a may contain?
a = randi(10, [1, 10]);
a(3) = 11;
a(a>2) = 12;
- 3, 4, 5, 6, 7, 8, 9, 10, 11, 12
- 1, 2, 12
- 2, 11, 12
- 1, 12
Q33. Which statement is true about the sparse matrices?
- You can use the sparse function to remove empty cells from cell array variables.
- Sparse matrices always use less memory than their associated full matrices.
- Mixtures of sparse and full matrices can be combined in all of MATLAB's built-in arithmetic operations.
- The sparse function requires its input to be a full matrix with at least 50% zero elements.
Q34. Which statement using logical indices will result in an error?
a = 1:10;
- b = a(a ~= 11)
- b = a(a == 1)
- b = a(a>6 && a<9)
- b = a(a | 1)
Q35. Which statement turns menu into the variable menu_string below?
menu = {'hot dog' 'corn dog' 'regular burger' 'cheeseburger' 'veggie burger'}
menu_string =
'hot dog
corn dog
regular burger
cheeseburger
veggie burger'
- menu_string = cell2mat(join(menu, newline))
- menu_string = cell2mat(join(menu, '\n'))
- menu_string = join(menu, newline)
- menu_string = cell2mat(pad(menu))
Q36. Which code snippet sets a new random seed based on the current time and saves the current settings of the random number generator?
- rng_settings_curr = rng('shuffle');
rng(time());
rng_settings_curr = rng();
- rng_settings_curr = rand('shuffle');
rng('shuffle');
rng_settings_curr = rng();
Q37. You have a matrix data in which each column is mono audio recording from a room in your house. You've noticed that each column has a very different mean and when you plot them all on the same graph, the spread across the y axis make it impossible to see anything. You want to subtract the mean from each column. Which code block will accomplish this?
- data_nomean = data - repmat(median(data), size(data, 1), 1);
- data_nomean = bsxfun(@minus, data, mean(data));
- data_nomean = zeros(size(data));
for i = 1:size(data, 1)
data_nomean(i, :) = data(i, :) - mean(data(i, :));
end
- data_nomean = zscore(data');
Q38. Which code block results in an array b containing the mean values of each array within C?
- b = zeros(1, size(C, 2));
for i_C = 1:size(C, 2)
b(i_C) = mean(C(i_C));
end
b = cellfun(@mean, C);
- b = zeros(1, size(C, 1));
for i_C = 1:size(C, 1)
b(i_C) = mean(C{i_C}(:));
end
- b = cellfun(@(m) mean(m(:)), C)
Q39. Which statement creates a logical array that is 1 if the element in passwords contains a digit and 0 if it does not?
passwords = {'abcd' '1234' 'qwerty' 'love1'};
- contains(password, '\d')
- ~isempty(regexp(passwords, '\d'))
- cellfun(@(x) ~isempty(regexp(x, '\d')), passwords)
- regexp(passwords, '\d')
Q40. Which is NOT a function that adds text to a plot?
- title
- text
- label
- legend
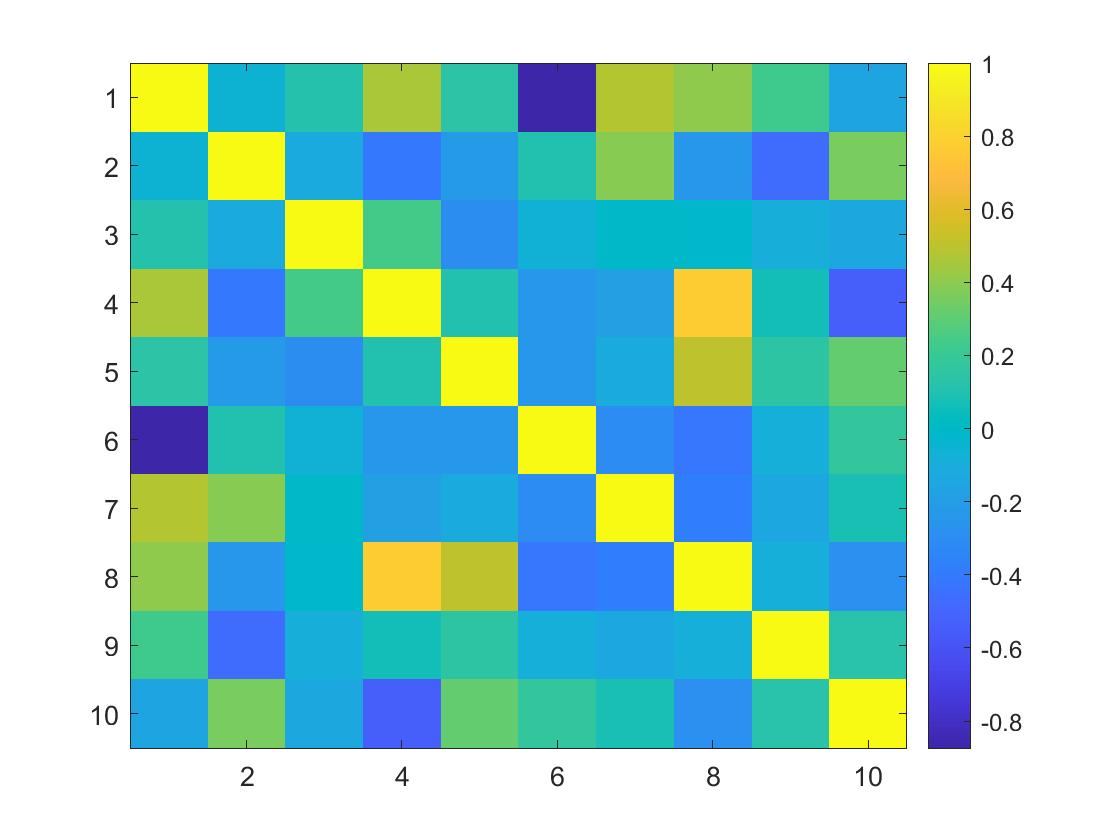
Q41. Which code block most likely produced this graph?
- [ ] figure
x = rand(10,10);
r = corrcoef(x);
surf(r)
colorbar
- [x] figure
x = rand(10,10);
r = corrcoef(x);
imagesc(r)
colorbar
Q42. What kind of files are stored with the .mat extension?
- figure files
- script files
- function files
- stored variable files
Q43. You would like to randomly reorder every element in array a and put the result into another array b. Which code is NOT necessary to do that?
a = 1:10;
- [ ] b = a(randi(10, 1, 10));
m = perms(a);
i = randi(factorial(10), 1);
b = a(m(i, :))
- [ ] [s, j] = sort(rand(10, 1));
b = a(i);
- [ ] b = a(randperm(10));
Q44. Which statement returns 1 (true)?
a = 'stand'
b = "stand"
- a == b
- ischar(b)
- length(a) == length(b)
- class(a) == class(b)
Q45. Which does E contain?
C = {'dog' 'cat' 'mouse'}
D = {'cow' 'piranha' 'mouse'}
E = setdiff(C,D)
- E = {'cat'} {'dog'}
- E = {'mouse'}
- E = {'cat'} {'cow'} {'dog'} {'piranha'}
- E =
Q46. Where in the UI can you see what variables have been created, their values, and their class?
- Editor
- command window
- details
- workspace
Read More About: Linkedin Quickbooks Quiz Answers
Q47. Given the following x and y coordinates, which choice calculates a linear regression for the x and y coordinates, and which plots the points of the x,y data and the regression line on the same graph?
x = 9.0646 6.4362 7.8266 8.3945 5.6135 4.8186 2.8862 10.9311 1.1908 3.2586
y = 15.4357 11.0923 14.1417 14.9506 8.7687 8.0416 5.1662 20.5005 1.0978
- [x] coeff_line = polyfit(x,y,1)
x_line = floor(min(x)):0.1:ceil(max(x));
y_line = polyval(coeff_line,x_line)
figure; plot(x,y,'o')
hold on
plot(x_linemy_line)
- [ ] figure
plot(x,y,'o')
coeff_line = polyfit(x,y,1);
x_line = floor(min(x)):0.1:ceil(max(x));
y_line = polyval(coeff_line,x_line);
plot(x_line,y_line)
- [ ] figure
plot(x,y)
coeff_line = polyfit(x,y,1);
x_line = floor(min(x)):0.1:ceil(max(x));
y_line = polyval(coeff_line,x_line);
hold on; plot(x_line,y_line)
- [ ] coeff_line = polyfit(x,y,1);
x_line = floor(min(x)):0.1:ceil(max(x));
y_line = polyval(coeff_line,x_line);
figure; plot(x,y,'o')
hold on
plot(x_line,y_line)
Q48. If you run this piece of code, you will get an error. Why?
a = [0 1 2 3; 4 5 6 7];
a = a^2;
- You are attempting to multiply a non-square matrix by itself, causing a dimension mismatch.
- MATLAB does not allow you to square all the elements in the matrix in a single operation.
- You must use the ** operator instead of the ^ operator.
- You cannot square matrices that have a 0 as the first element.
Related Posts:




Comments
Post a Comment